On this page
The webinar discusses the challenges and complexities in product management, emphasizing the need to navigate ambiguity and uncertainty. The speaker, Phil, shares his experiences and insights, focusing on the importance of strategic clarity, efficient solutions, and aligning business success with customer outcomes. He outlines the pitfalls of focusing solely on output metrics and highlights the need for effective communication and goal setting. Phil also discusses the impact of unclear strategies on user experience and team morale, and shares principles and lessons from his personal experiences.
How does it apply to you?
This blog serves as a guide for new and seasoned software developers and product managers. It provides insights into navigating ambiguity and uncertainty, the importance of strategic clarity, focusing on outcomes rather than outputs, and how to align business success with customer outcomes. These principles can be applied in both personal and professional situations, helping individuals and teams to make better decisions and create more effective software.
Developer Checklist
Strategic Clarity and Goal Setting
Product Management
Team Management and Communication
Learning and Adaptation
Summary
Introduction and Background
Phil, the speaker, introduces himself as the current PM leading the iOS growth team on Google Photos. He shares his past experiences working on YouTube TV's advertising platform and Google messages on Android, focusing on the conversation experience and growing RCS adoption. He expresses his interest in meeting founders and helping with growth, product marketing, and go-to-market strategies. He clarifies that all the opinions shared in the discussion are his personal views and do not represent Google's stance.
Navigating Ambiguity and Uncertainty
Phil discusses the core part of the product management experience, which is navigating ambiguity and uncertainty, especially in strategic decision-making. He highlights the importance of a product manager's ability to enable their teams to identify opportunities and execute them effectively. He emphasizes that uncertainty is a common aspect of product management and is often where interesting challenges and innovation arise.

Lessons from Personal Experience
Phil expresses his intention to share lessons, mistakes, and principles drawn from his personal experiences. He believes these principles apply across different decision-making scenarios and across different flavors of product management. He aims to provide specific, practical steps to embody these principles, focusing on defining the right goals, effective communication, and maintaining team morale.




Challenges in New Product Management Roles
Phil paints a picture of the challenges one might face in a new product management or growth leadership role. Despite initial excitement and a wealth of theoretical knowledge, new PMs often find the task much harder than expected. He emphasizes that there's no foolproof recipe for reliably acquiring new users or improving retention, and that strategic clarity is crucial for team success.

Symptoms of Poor Strategic Clarity
Phil outlines the problems that can arise when teams lack strategic clarity. These include difficulty in prioritizing tasks due to ambiguity about which activity will drive the most impact, and misalignment within teams as individuals rely on their personal opinions rather than aligning towards a shared purpose. This can lead to different teams prioritizing different outcomes, which may not be optimal for the organization.
Impact of Unclear Strategy on UX and Team Morale
When a business strategy isn't clear, it can lead to a muddied user experience (UX) and inconsistent choices made by the team. This lack of strategic clarity can lead teams to overly focus on short-term results, craving certainty over long-term value creation. Over time, this over-optimization can lead to diminishing returns on efforts, negatively impacting team morale. This can make the work feel burdensome, and even high performers may leave if they don't believe in, understand, or feel they can execute the strategy.
Identifying Deficiencies in Strategy
Signs of deficiencies in strategy may include lack of alignment on goals, ineffective communication of goals and approach, and poor management of the team's relationship with uncertainty. Successful teams and leaders often overcome these challenges by resolving these issues.

Defining the Right Goals
It's important to focus on outcomes, not just outputs. This concept is illustrated with a model where customers interact with a product, leading to changes in behavior measured by output metrics like daily active users, retention, revenue, and lifetime value. However, this model can become problematic when used as a tool to prioritize and plan. For instance, a hypothetical example of a shovel rental business shows how optimizing for an output metric like retention could lead to a worsened product.

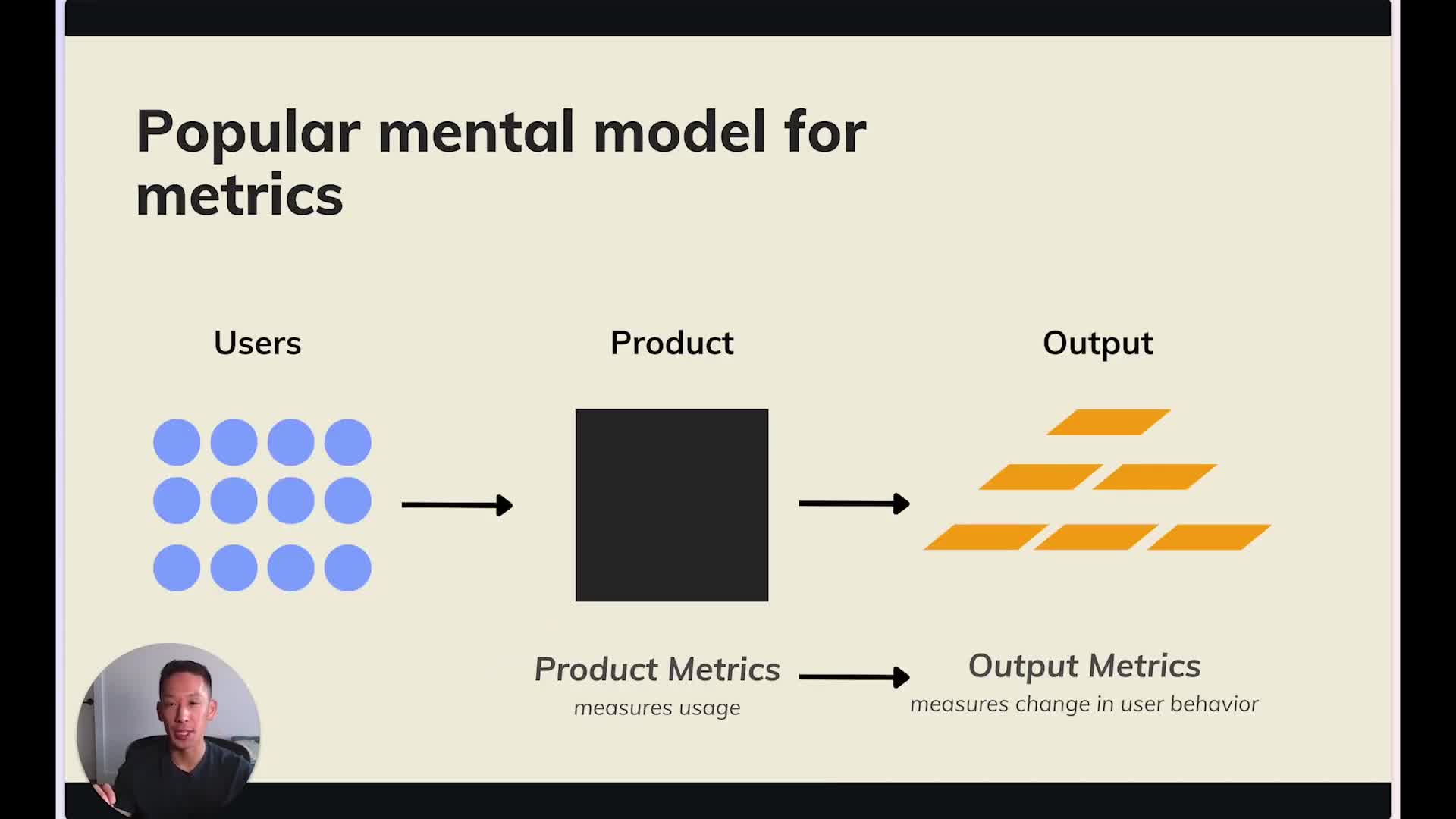
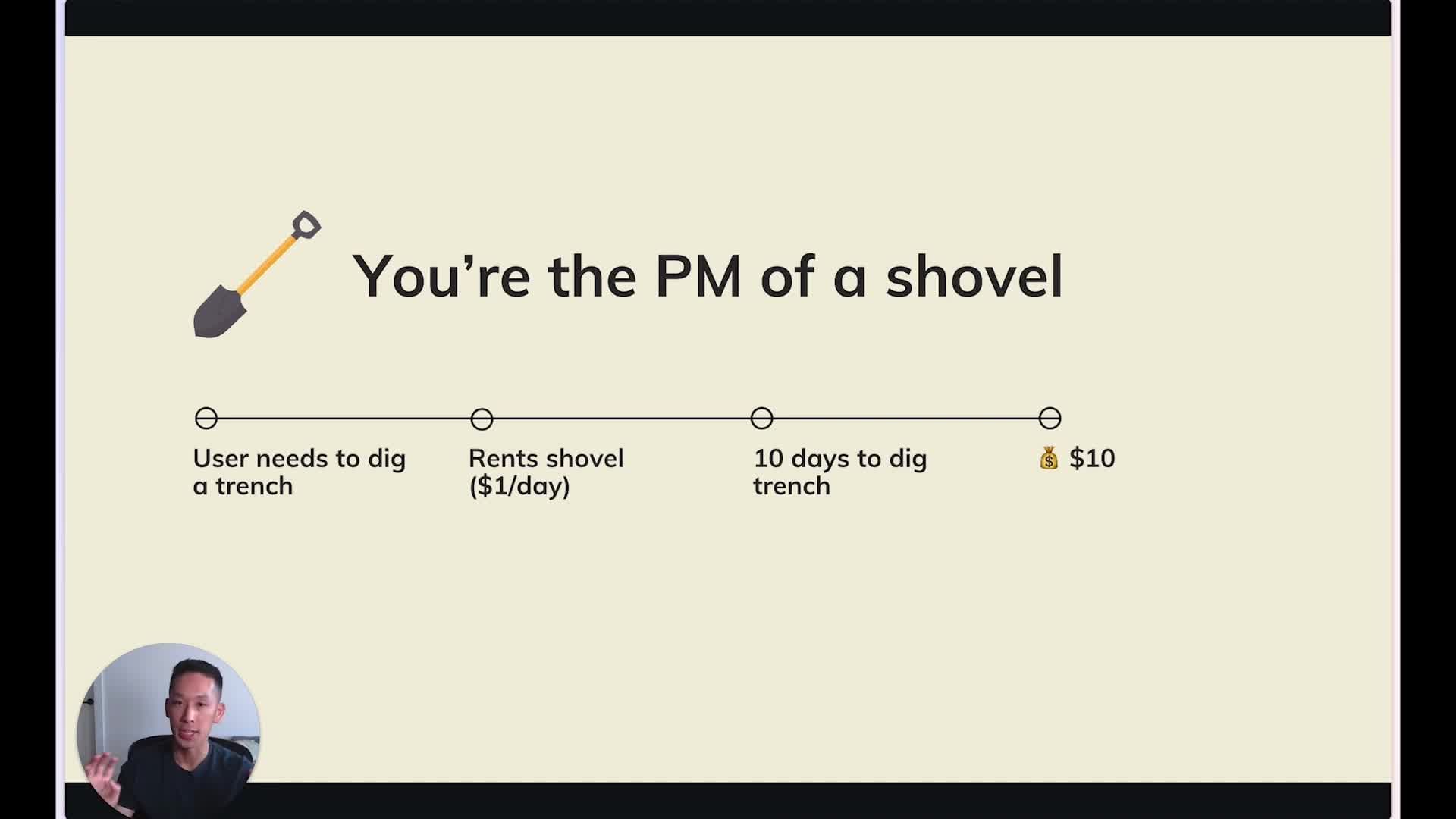
The Pitfalls of Focusing on Output Metrics
Starting with an output metric and working backwards to optimize it can lead to problems. This approach defines success based on the specifics of a solution rather than the underlying outcomes that people actually care about. For instance, a person evaluates medicine by how effectively it can solve a health issue, not by how often they need to take it.
Emphasis on Outcome Over Training
The importance lies in the behavior of the dog, not the hours of training it received. This analogy is used to highlight the need to prioritize outcomes over the process. The goal is to complete tasks faster, cheaper, and easier. The focus should be on the context and the situation in which the solution operates. The value of a solution is dependent on its efficiency and its fit into specific contexts.
Efficiency as a Value Driver
Efficiency is the fundamental thing that drives value. Users prefer solutions that are faster, cheaper, and easier. If a product isn't more efficient than an alternative, users won't be motivated to use it. Long-term user retention requires an efficient solution that can overcome users' inertia, laziness, and fears.
Aligning Business Success with Customer Outcomes
There can be a conflict between the value provided to customers and the value accrued as a business. This conflict should be surfaced and resolved to align the success of the business with customer outcomes. The viability of a business is determined by how well it can align its success with the outcomes of the customer.
Complexity of Products and Businesses
Products and businesses are complex, and the top line metric is rarely straightforward. Metrics are proxies for outcomes, and treating complex problems as though they are well-structured can be misleading. While quantitative metrics are still necessary, qualitative thinking should not be overlooked when defining goals.
Thinking about User Outcomes
Thinking about user outcomes aligns the success of a product with what users value. This involves understanding the problem being solved, the frequency of that problem, and the expected behavior within the context users are operating under.

Building Roadmaps
Traditional roadmaps can provide an illusion of certainty in an ambiguous situation. However, they can become prescriptive, dictating teams' actions and encouraging a focus on launching features by a certain date, even when circumstances change. The OKR process attempts to give teams more flexibility, defining the outcomes and metrics to be achieved.
Challenges in Leadership and Decision-Making
Leaders often struggle with allowing their teams the freedom to make decisions and define their own paths to achieving key results and objectives. The natural inclination is to control the process, dictating actions, launches, and timelines. This is often due to a desire for certainty and a fear of ambiguity. However, it's crucial to resist this urge and instead provide teams with latitude to explore and innovate. This challenge is particularly pronounced in ambiguous problem spaces, where the path to the desired outcome is not clear.
Importance of Communication Tools
Leaders should view tools like roadmaps as communication aids rather than contracts. The key role of product leaders is to find effective ways to communicate progress while acknowledging the realities of an uncertain path. The Opportunity Solution Tree, popularized by Teresa Torres, is one such tool that provides a visual representation of the plan to achieve a desired outcome.

Components of the Opportunity Solution Tree
The Opportunity Solution Tree consists of three main components: the desired outcome, opportunities, and solutions. The desired outcome is the goal your project needs to achieve. Opportunities are pain points that can be addressed to help users achieve the desired outcome. These should be based on evidence, not just intuition or assumptions. Solutions are ideas for addressing these pain points, as well as the experiments, assumptions, and hypotheses you want to validate or disprove.
Applying the Opportunity Solution Tree
The Opportunity Solution Tree helps visualize multiple paths to achieving the desired outcome and forces teams to acknowledge what they know now versus what they need to find out. This is particularly useful when dealing with ambiguous problems. The example provided involves a ride-sharing app aiming to increase the number of successful rides where a user is happy with the whole experience. Through the Opportunity Solution Tree, the team identifies several opportunities (reducing cancelled rides, ensuring rides don't take longer than expected, improving ride comfort) and formulates hypotheses to test solutions.

Lowering Pickup Times for Short Trips
The discussion revolves around a thought process to improve user experience by reducing pickup times for short trips. This is hypothesized to make the trip feel faster and thus increase user satisfaction. The idea is to run a minimum viable test to validate this hypothesis. For a certain group of users, within a specific timeframe, drivers would prioritize picking up those who have called for shorter trips. The hypothesis would be considered valid if there is a 10% increase in five-star ratings from users who have taken these prioritized short trips.
Assessing and Updating the Opportunity Solution Tree
Post-experiment, the results are surfaced on the Opportunity Solution Tree (OST). There's an emphasis on being inquisitive and asking questions like whether the opportunity is larger or smaller, more or less actionable, and whether the problem has become easier or harder to solve. This process helps decide if the opportunity is still right to pursue or if there's a need to update or cross off completely different parts of the OST. The OST is not a magical framework that solves every challenge, but it helps embrace a strategy based on user outcomes and hypotheses.
Embracing Uncertainty in the Discovery Process
The framework embraces the unknown as a natural part of the discovery process. Uncertainty is not something that needs to be eliminated at all costs. The framework helps build a roadmap driven by hypotheses and provides a shared language and set of practices to flexibly adapt to reality.

Operating Transparently and Predictably
The importance of operating transparently and predictably is highlighted. This is due to the sobering statistic that only about 10 to 20 percent of experiments lead to expected results. Instead of brushing 'failures' under the rug, it's essential to maximize learnings from these experiences. Sharing these learnings widely, even when things don't go as planned, can be beneficial in ways that might not have been anticipated.

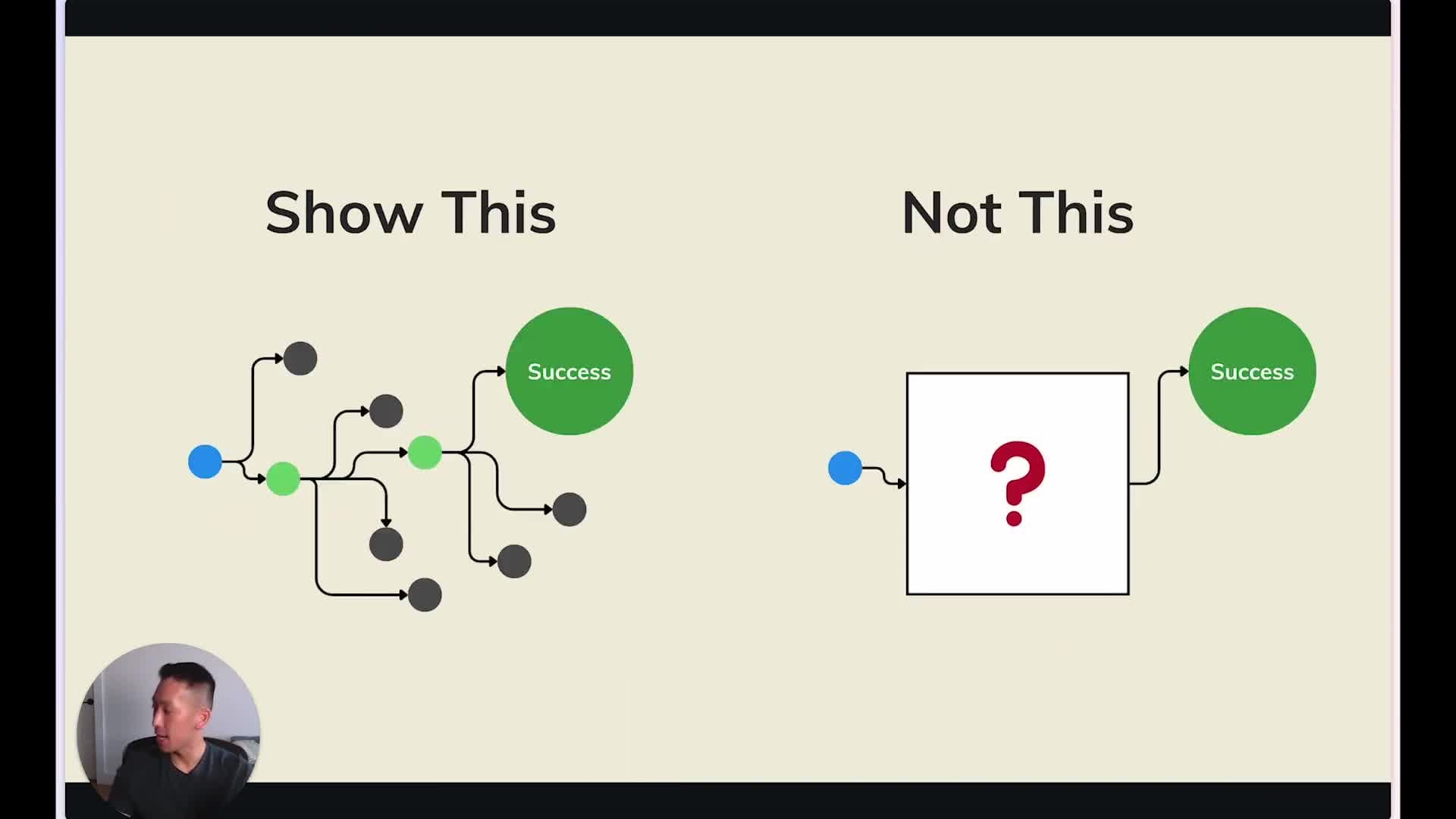
Building Trust Through Transparency
Being transparent, detailing the rationale behind decisions, and articulating what happened can build trust. This trust is powerful in countering people's anxiety and impatience. Being consistently transparent, even when admitting mistakes, can make people feel invested and gain confidence in the process and the leader.

Control and Execution in a Team Setting
Emphasizes the importance of focusing on factors within the team's control, such as effective execution and rapid learning. Encourages thoughtful scoping of experiments and clear communication of thought processes and next steps. Stresses the importance of setting a positive example and maintaining engagement and excitement within the team.

Maximizing 'Shots on Goal'
Advocates for maximizing opportunities or 'shots on goal' to increase the likelihood of success. This involves continuous learning and iteration to get closer to goals. Emphasizes the competitive advantage of understanding users and markets and effectively identifying and seizing opportunities.
Learning Reviews as a Valuable Tool
Introduces the concept of learning reviews, which focus on what has been learned rather than just what has been achieved. Proposes five key questions for these reviews: what did we try, what did we think was going to happen, what actually happened, what did we learn, and what are we going to do next. Emphasizes the value of a learning-focused approach.

Key Takeaways and Principles for Success
Recaps the key takeaways: focusing on outcomes not outputs, using a roadmap as a communication tool, creating a culture that celebrates learning, and navigating ambiguity by embracing the unknown. Emphasizes the importance of controlling how the team approaches each day and how effectively they learn and celebrate their learnings.
Closing Remarks and Invitation for Connection
Encourages listeners to connect on LinkedIn for further discussion, guidance, or consulting related to product management and growth. Expresses enthusiasm for working with product leaders and founders, particularly in areas related to product growth, marketing, and go-to-market strategy.
FAQs
Who is Phil and what is his role at Google? Phil is the current PM leading the iOS growth team on Google Photos. He has past experiences working on YouTube TV's advertising platform and Google messages on Android.
What is the core part of the product management experience according to Phil? The core part of the product management experience is navigating ambiguity and uncertainty, especially in strategic decision-making.
What are some challenges faced in new product management roles? New PMs often find the task much harder than expected. There's no foolproof recipe for reliably acquiring new users or improving retention, and strategic clarity is crucial for team success.
What are the symptoms of poor strategic clarity? Symptoms of poor strategic clarity include difficulty in prioritizing tasks due to ambiguity about which activity will drive the most impact, and misalignment within teams.
What is the impact of unclear strategy on UX and team morale? Unclear strategy can lead to a muddied user experience (UX) and inconsistent choices made by the team. Over time, this over-optimization can lead to diminishing returns on efforts, negatively impacting team morale.
What signs indicate deficiencies in strategy? Signs of deficiencies in strategy may include lack of alignment on goals, ineffective communication of goals and approach, and poor management of the team's relationship with uncertainty.
What is the importance of focusing on outcomes, not just outputs? Focusing on outcomes rather than outputs ensures that success is defined based on the underlying outcomes that people actually care about, not just on the specifics of a solution.
What are the pitfalls of focusing on output metrics? Starting with an output metric and working backwards to optimize it can lead to problems. This approach defines success based on the specifics of a solution rather than the underlying outcomes that people actually care about.
What is the importance of efficiency as a value driver? Efficiency is the fundamental thing that drives value. Users prefer solutions that are faster, cheaper, and easier. Long-term user retention requires an efficient solution that can overcome users' inertia, laziness, and fears.
How can business success be aligned with customer outcomes? The success of a business can be aligned with the outcomes of the customer by surfacing and resolving any conflict between the value provided to customers and the value accrued as a business.
What does thinking about user outcomes involve? Thinking about user outcomes involves understanding the problem being solved, the frequency of that problem, and the expected behavior within the context users are operating under.
What is the downside of traditional roadmaps? Traditional roadmaps can provide an illusion of certainty in an ambiguous situation. However, they can become prescriptive, dictating teams' actions and encouraging a focus on launching features by a certain date, even when circumstances change.
What is the Opportunity Solution Tree? The Opportunity Solution Tree is a tool that provides a visual representation of the plan to achieve a desired outcome. It consists of three main components: the desired outcome, opportunities, and solutions.
How can the Opportunity Solution Tree be applied? The Opportunity Solution Tree helps visualize multiple paths to achieving the desired outcome and forces teams to acknowledge what they know now versus what they need to find out. This is particularly useful when dealing with ambiguous problems.
What is the importance of operating transparently and predictably? Operating transparently and predictably is important because only about 10 to 20 percent of experiments lead to expected results. Instead of brushing 'failures' under the rug, it's essential to maximize learnings from these experiences. Sharing these learnings widely, even when things don't go as planned, can be beneficial in ways that might not have been anticipated.
How can trust be built through transparency? Being transparent, detailing the rationale behind decisions, and articulating what happened can build trust. This trust is powerful in countering people's anxiety and impatience. Being consistently transparent, even when admitting mistakes, can make people feel invested and gain confidence in the process and the leader.
What is emphasized in control and execution in a team setting? In a team setting, it is important to focus on factors within the team's control, such as effective execution and rapid learning. It also encourages thoughtful scoping of experiments and clear communication of thought processes and next steps. It stresses the importance of setting a positive example and maintaining engagement and excitement within the team.
What does maximizing opportunities involve? Maximizing opportunities involves continuous learning and iteration to get closer to goals. It emphasizes the competitive advantage of understanding users and markets and effectively identifying and seizing opportunities.
What is the concept of learning reviews? Learning reviews focus on what has been learned rather than just what has been achieved. They propose five key questions: what did we try, what did we think was going to happen, what actually happened, what did we learn, and what are we going to do next.
What are the key takeaways for success? The key takeaways for success are focusing on outcomes not outputs, using a roadmap as a communication tool, creating a culture that celebrates learning, and navigating ambiguity by embracing the unknown.
How can you control the team's approach to each day? You can control the team's approach to each day by effectively learning and celebrating their learnings.
How can listeners connect for further discussion, guidance, or consulting related to product management and growth? Listeners are encouraged to connect on LinkedIn for further discussion, guidance, or consulting related to product management and growth.





